Law of supply depends upon prices because the quantity of goods supplied rises as market price rises, as the prices falls the quantity of goods supplied falls. There is direct relationship between quantity supply and prices. On the other hand, law of demand says that quantity of goods demand rises as price falls and the demand falls as price rises. There is indirect relationship between prices and quantity demanded. Relationship between price and quantity demanded is recognized as the demand relationship.
Law of Supply: -
The supply law is the microeconomic law. It states that when the price of goods raises the quantity of goods will increase. The Law of supply says that as the price of goods rises, sellers will try to exploit their returns by increasing the quantity offered for sale.
Factors that affect supply: -
In the above instance, supply only considers the supply creates by a single corporate. In actual economies, supply is based upon many other factors. Manufacture capability, manufacture prices such as labor and resources, and the number of participants directly distress how a much supply productions can create. Ancillary reasons such as material obtainability, climate and the reliability of supply chains can also distress supply
Law of Demand: -
Demand is an economic norm that defines a customer’s willingness to pay a price for a good or service. A rise in the price of a good or service will fall demand. Demand as your willingness to go out and purchase a certain product. For example, Market demand is depending upon what everyone in the market wishes.
Factors that affect Demand: -
Demand is affected by the quality and price of a product. The number of accessible alternatives, publicity and moves in the price of complementary products also distress its demand. For instance, if the price of video game comfort drops, demand for games for that comfort may rise as more individuals buy the comfort and want games for it.
Aggregate supply: -
Total supply, also known as aggregate production, is the total quantity of goods and services produced within an economy at a specified price level in each time. It is denoted by the total supply curve, which defines the relationship among price levels and the quantity of output that firms are willing to provide. There is a positive relationship among aggregate supply and the price level.
Causes of shifts aggregate supply: -
Shift in total supply can be attributed to a number of variables. These include changes in the size and worth of labor, technological modernizations, increase in incomes, and rise in manufacture costs, changes in manufacturer taxes and subsidizations, and changes in inflation. These dynamics lead to optimistic changes in aggregate supply, while others cause aggregate supply to drop.
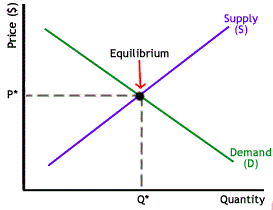
Equilibrium in economics: -
The Quantity of an item that will be demanded at the point of economics equilibrium is equal to the quantity that will be supplied is called economics equilibrium. This point is determined by observing the crossing of supply and demand curves.
Equilibrium of law of demand and supply: -
When the goods demanded are equal to goods supplied it is called equilibrium. Everyone is fulfilled from this economics situation. At this stage dealers are selling all the goods that they have bent and consumers are getting all the goods that they are demanding.
Equilibrium Price in demand and supply: -
The stability price is the price at which the manufacturer can sell all the items he desires to create, and the consumer can buy all the units he desires. A Simple illustration of how supply and demand decide balance price, imagine a corporate brings out new merchandise. It sets a high price, but only a limited customer bargain it. The corporate expected selling more items, but due to absence of interest, it has stores full of the product. Due to its high supply, the corporate depresses the price. Demand rises, but as the industries supply decreases, it increases the price till it finds the perfect price to balance its supply with customer demand.
Market Disequilibrium: -
Disequilibrium occurs if the market is not in stability. More precisely, market disequilibrium occurs if the demand price is not equal to the supply price and the quantity demanded is not equal to the quantity supplied. In general, disequilibrium occurs if conflicting forces are not in stability.
July 17, 2017